
Types of HVAC Systems: From Homes to Industrial Cooling
When people talk about HVAC systems, they could be referring to very different setups. For a homeowner, it might mean a split AC in the living room. For a hotel, it could be a network of fan coil units connected to a chiller. And for an industrial plant, it may mean a customized process cooling system running 24/7.
Understanding the different types of HVAC systems helps homeowners, consultants, and facility managers choose the right solution a critical decision across the GCC and Middle East, where cooling demand is among the highest in the world.
What Does HVAC Mean?
HVAC stands for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Add refrigeration and you get HVACR, a term that covers everything from small window ACs to massive industrial chillers. At its core, every system aims to:
- Control air temperature (heating or cooling)
- Manage indoor air quality (ventilation and filtration)
- Preserve goods or processes (refrigeration, cold storage systems)
Common HVAC Systems for Homes and Offices
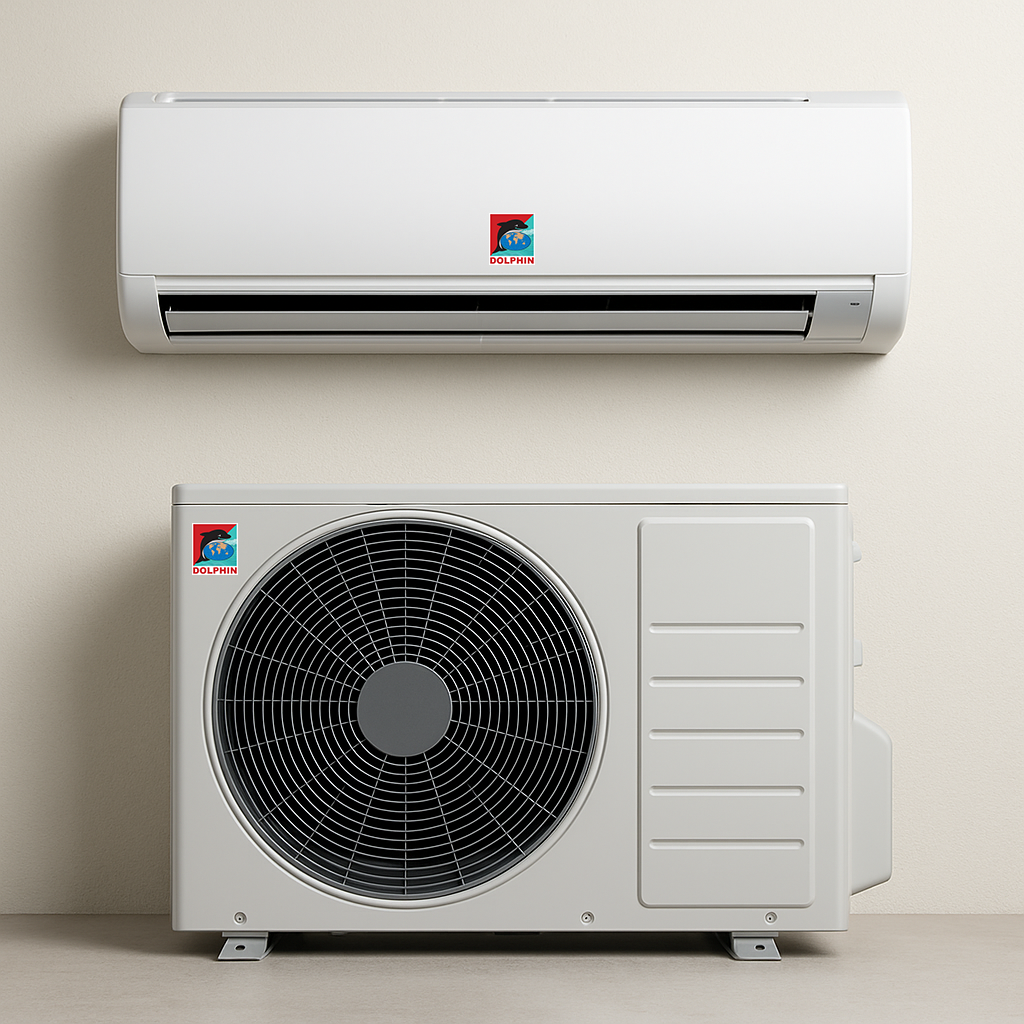
Split AC and Window AC
Split ACs use an indoor unit and outdoor condenser, while window ACs package everything into a single unit. Both are popular in residential and small office settings.
Ducted Units and Inverter ACs
For larger homes and offices, ducted systems distribute air evenly through concealed ducts. Inverter ACs adjust compressor speed for greater efficiency, reducing energy consumption over time.
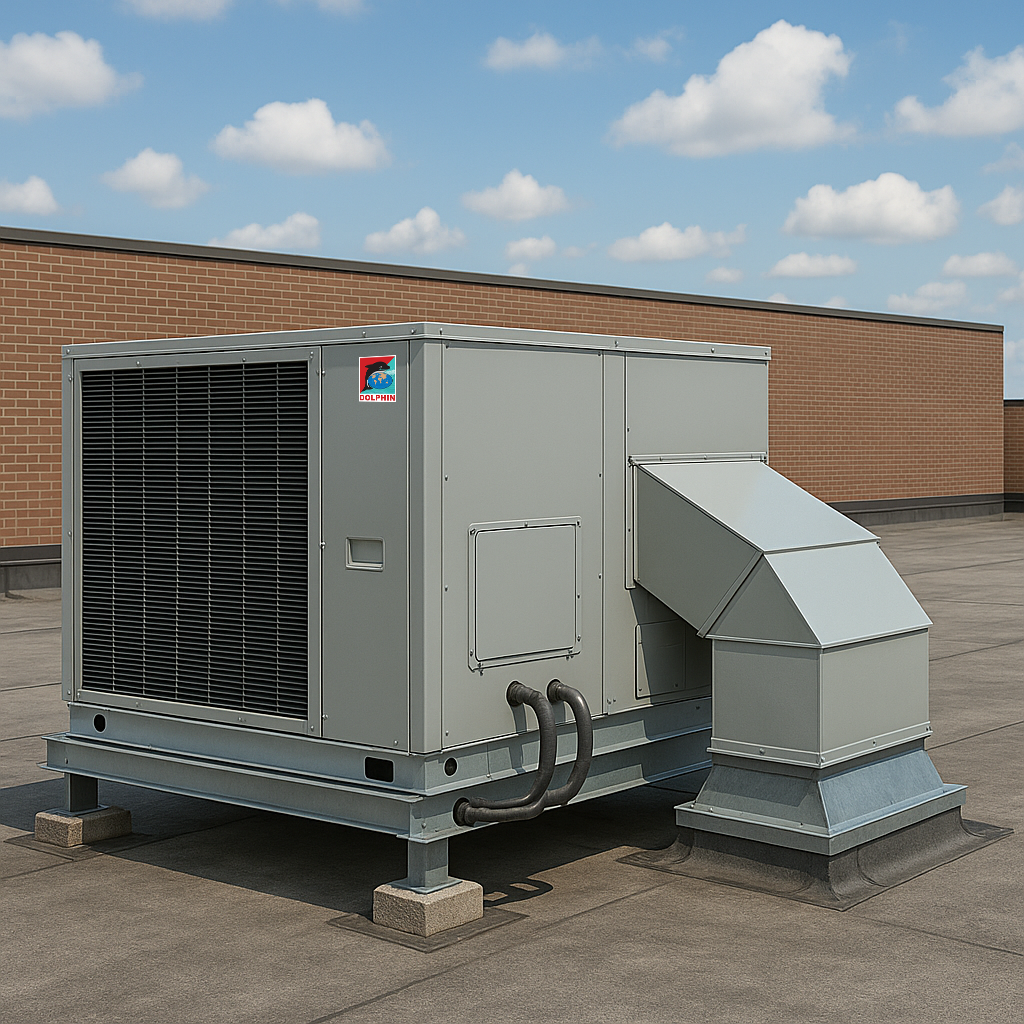
Packaged and Roof to Units
For mid-sized buildings, packaged units and rooftop units provide central cooling without requiring a full chiller plant. These are commonly used in schools, retail outlets, and low-rise commercial spaces.


Common HVAC Systems for Homes and Offices
VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow)
VRF systems allow multiple indoor units to operate from a single outdoor system. They offer zone-by-zone control, making them ideal for hotels, offices, and mixed-use developments. Their energy efficiency is especially valuable in the GCC, where cooling loads are high.
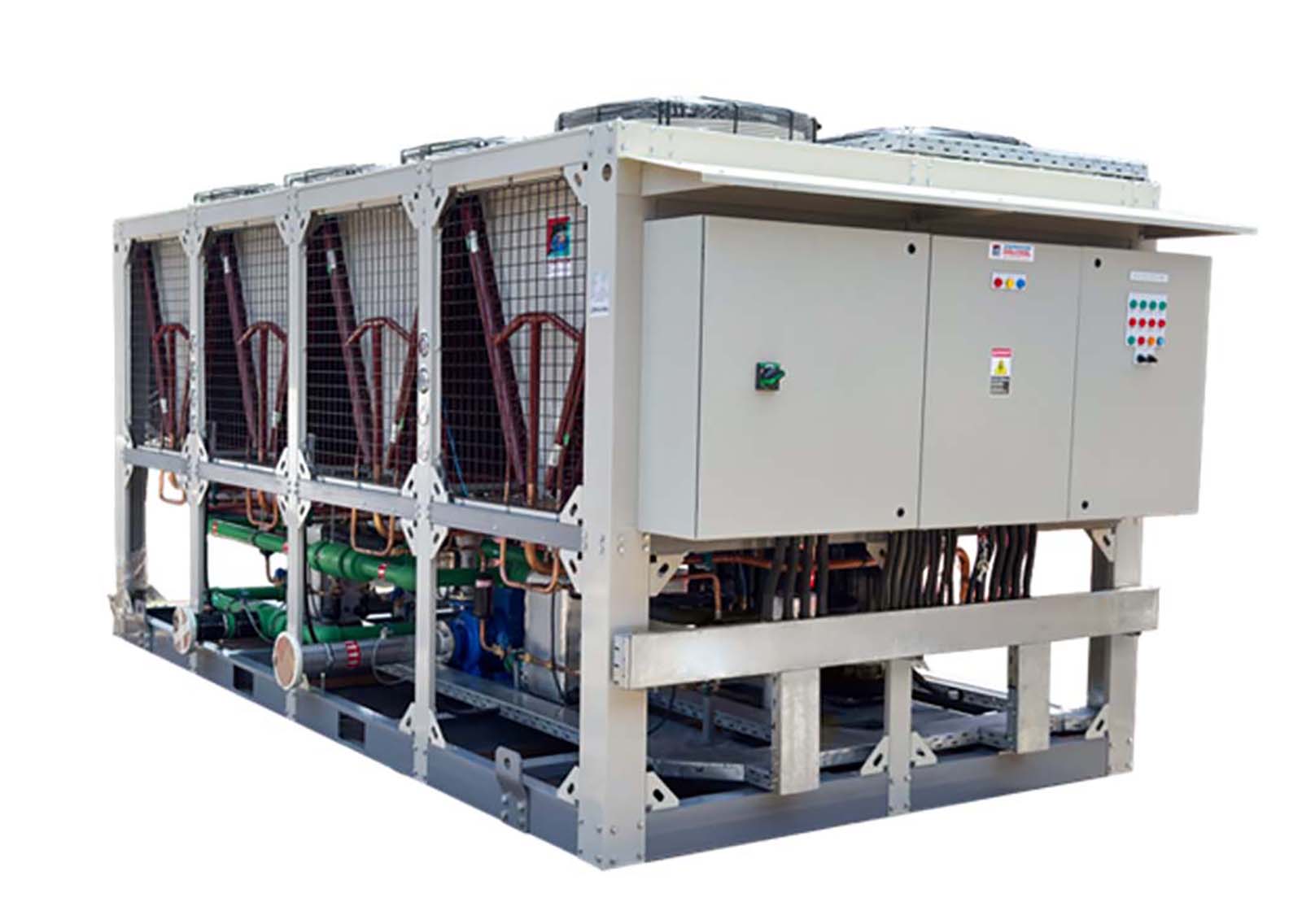
Chillers
Chillers form the backbone of large-scale cooling systems. They use chilled water loops to provide consistent cooling to entire buildings, airports, malls, or industrial facilities. In the Middle East, chillers are among the most critical HVAC systems due to large building footprints and year-round cooling demand.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps can both heat and cool, making them highly versatile in climates with seasonal variations. While not common in the Gulf, they play a major role in other regions where heating demand is higher.


Industrial HVAC and Specialized Systems
Beyond comfort cooling, industrial HVAC systems are designed for mission-critical environments:
- Process cooling in manufacturing plants
- Cold storage systems for food, pharmaceuticals, and logistics
- Specialized cooling units for data centers and high-tech facilities
Choosing the Right HVAC System
The right choice depends on:
- Scale: A villa vs a shopping mall vs an industrial facility
- Environment: Hot and humid Gulf conditions vs colder climates
- Application: Comfort cooling vs precision cooling vs cold storage
- Energy Efficiency: Systems like inverter ACs and VRF reduce long-term costs
For small homes, a split AC may be enough. For malls and airports, it’s often a chiller system with VRF support. For warehouses and factories, industrial HVAC with cold storage systems becomes essential.
From window ACs in residential units to chillers in mega-projects, HVAC systems come in many forms each designed for a specific need. In the GCC and Middle East, where cooling is a necessity, choosing the right system ensures comfort, efficiency, and reliability.
For consultants, contractors, and facility managers, understanding the variety of HVAC systems is the first step to specifying the right solution for every project.
